Cryptocurrency and blockchain have already made their way into the books of many small and big companies. They have evolved from being some form of dubious technologies to becoming the next-generation tech that are key to driving the next industrial revolution.
Both cryptos and blockchains offer promising use cases to finance, supply chain, internet security, cloud storage, and a number of other sectors.
But when we discuss any technology for the future, sustainability is a crucial factor. We are at the tipping point of environmental damage and a technology that threatens the remaining balance in our ecosystem can prove devastating in the long run.
As is the case with most cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies today, they do not fit the mold of a sustainable future solution for money. While fiat currencies are a threat because they are paper-based, cryptocurrencies may have lethal consequences for our environment due to their extensive energy consumption.
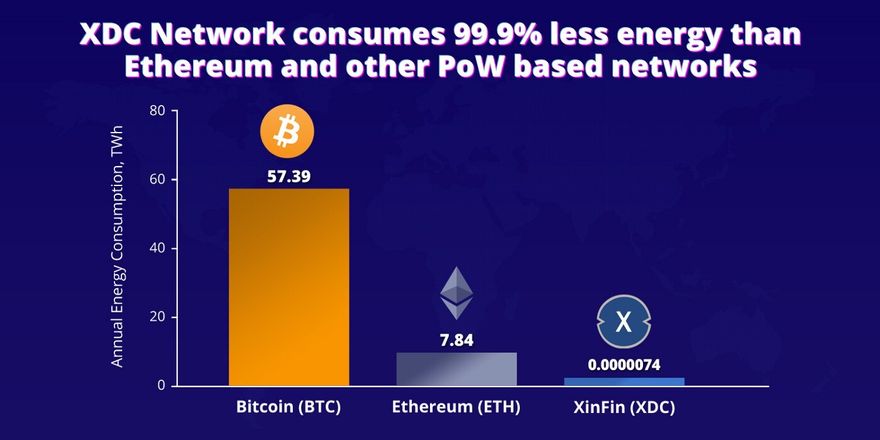
The Bitcoin network alone consumes almost 0.21% of the world’s total energy supply, which is equivalent to 57.3 terawatt-hours. To put that into perspective, this equals the annual energy consumption of Switzerland. Ethereum network, on the other hand, consumes more than 7.8 terawatt-hours of electricity, which makes Ether the second most energy-intensive blockchain network and cryptocurrency. Recently, Bill Gates also raised concern on climate change and its effect on the environment in his Blog he says “To understand the kind of damage that climate change will inflict, look at COVID-19 and spread the pain out over a much longer period.”
So, why do most cryptocurrencies consume such huge amounts of energy? The answer lies in the underlying consensus protocol.
Proof-of-Work
Proof-of-Work or PoW is an algorithm that a decentralized network uses to settle transactions on a blockchain network. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ether employ the PoW consensus algorithm to create new coins and also distribute the coins across the network.
In the PoW algorithm, blockchain nodes called miners from across the world use high-end computing hardware to solve cryptographic puzzles to approve transactions and mine new coins. Each blockchain node competes against all other nodes to be the first to generate the hash that is the solution for the puzzle. As they solve the puzzle and approve transactions, they mine a new block on the network and also create new crypto coins. The winning node gets to claim the new coin that mined on the network.
Earlier, it was possible to mine Bitcoin using the RAM of a personal computer. With time, however, the mining difficulty on the Bitcoin network has increased multifold. Today, we have application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) devices developed for the sole purpose of mining Bitcoin and other PoW-based cryptocurrencies. Each of these devices can have an environmental cost of up to $1,500 per year. (Source)
It is expected the energy demand of these PoW networks will keep growing as the networks grow in size and more blocks and transactions are added to them.
How XDPoS Solves the Energy Problem of Cryptocurrencies?
To solve the energy challenge presented by traditional cryptocurrencies using PoW consensus algorithm, blockchain pioneers developed the Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) mechanism. The DPoS is a variation of the Proof-of-Stake consensus and is touted as a more energy and time-efficient alternative to other consensus protocols.
While DPoS consensus is a topic of much debate due to its pseudo-decentralization, the XinFin Network uses an exclusive version of DPoS that promises decentralization, scalability, and low energy consumption at the same time.
The XinFin Hybrid Blockchain uses the XDPoS protocol to validate and add transactions on the ledger. To ensure maximum decentralization and security of the transactions, XinFin’s XDPoS protocol uses real-time voting to elect a pool of validators. It prevents any set of nodes from carrying out a pre-planned attack on the network.
XDPoS makes XinFin’s XDC coin a “green coin.” Unlike other cryptocurrencies, XDC coins are pre-mined and hence do not require high electricity consumption. This also makes the network more scalable, allowing a transaction speed of almost 2,000 transactions per second.
Compared to other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ether, the energy consumption of XDC is almost negligible. Where Bitcoin and Ethereum’s electricity consumption surmounts 57.3 and 7.84 TWh respectively, the XDC coin only uses 0.000007446 TWh or just 7,446 kWh of electricity.
The annual cost for approving transactions and distributing XDC coins will stand approximately at just $600 as on 12th August 2020. (source).
Parting Thoughts
If we are looking for a sustainable technology solution for both decentralized networks and a new form of an economic model, it is fundamental that they are energy efficient. And as we saw above, PoW coins are far away from being a fit. XDPoS, on the other hand, solves the problem by reducing energy consumption by thousands of times. It can be said that coins that rely on such sustainable consensus algorithms will be the future of the crypto economy and a decentralized future.
Source of technical information:
XinFin Public XDPOS Consensus - XDPoS
Explore XDPoS based Tools:
XDC Chain Network Tools and Documents
Grab the opportunity of Bounty programs:
You can store your XDC at XDC Web Wallet, Also you can download Android Wallet







Discussion (0)