A subnet in the blockchain is a smaller network that allows users to segregate their network traffic. It allows for implementing different security measures, such as firewalls, and provides a means for scaling up the blockchain network. Subnets also allow for certain parts of the blockchain to remain private, providing a safer environment for confidential transactions. Subnets can be beneficial in providing increased capacity when the demands of the wider blockchain network become too much. Overall, subnets are a useful tool that can help increase the efficiency of a blockchain network.
So, what exactly are subnets in the context of blockchain technology? Simply put, a subnet is a separate, independent network. They are usually a part of a larger blockchain network. These subnets are connected to the main network but operate independently and have rules and protocols. Often they inherit the properties of the parent blockchain network. For example, a subnet within the XDC network running XDPOS 2.0 will usually run the same consensus mechanism, leading to fast transaction speeds and low finality times.
Most people know XinFin XDC Network as an EVM-compatible blockchain that has gained significant traction. However, there is much more to XinFin XDC Network, including many more blockchains!
Many XDC Network users are only familiar with the main network, which forked off the Ethereum Geth client to add support for the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). but there is a XinFin XDC Network Primary Networks. But in addition, one of XinFin’s core innovations is the ability to create highly scalable and customizable blockchains called Subnets.
With limited block space and demand rising, fees have risen on the other Chain. And while there are improvements that can be made, scaling to meet demand requires more blockspace or more efficient use of existing blockspace (i.e., off-chain computation via Layer 2s). Subnets are XinFin XDC Network is the solution to this problem.
Instead of forcing all transactions to take place in a single, shared state, Subnets allow developers to launch their own blockchains– creating more blockspace and computation to meet demand.
For more details, please check out How to Set Up a Private Blockchain Network with XDC Network Codebase
What’s a Subnet?
Subnets, or subnetworks, are dynamic subsets that reach consensus on their blockchains. This definition can feel somewhat formal, so jargon aside, Subnets are effectively ‘Blockchain-as-a-Service’ secured by some portion. Put another way, and a Subnet is not a blockchain; a Subnet is a group of validators. Today, all Subnets (other than the Primary Network) run a single blockchain, but it is possible for future Subnets to run multiple blockchains.
When a subnet is used in blockchain, it provides a secure way to store and transfer data, thus increasing the system’s safety. Subnets also provide a way for transactions to be conducted quickly and reliably, which is essential for a blockchain system to operate efficiently. Subnets are also important for scalability and interoperability, as the network can be easily divided into multiple sections, allowing for faster and more secure transactions. Ultimately, subnets in blockchain are essential for creating a secure and reliable system and allowing the technology to be used in a wide range of applications.
XinFin XDC Network masternode doesn’t automatically run blockchains for any Subnet. Instead, Subnets need to create a masternode separately for their support. Since Subnets can have their economies with their native tokens and free markets, it is likely that Subnet masternode will stake and be rewarded in a Subnet’s native token.
Once a user creates a Subnet, the Subnet can create rulesets for their masternode and launch their blockchains with customized virtual machines. Since the developers can customize various aspects of how the underlying chain operates, they can also implement features like sending gas fees to a treasury smart contract or requiring all chain users to pass through KYC before interacting with applications on the Subnet.
It was originally envisioned that Subnets would be a hub for financial markets to launch highly customized and permissioned systems. However, in practice, many of the current teams interested in launching Subnets are looking to scale their existing applications, which might be limited by their current chain.
Limited by their current chain, these live projects might not be as interested in modifying the underlying blockchain. For these builders, they can simply run a copy of an existing virtual machine, deploy their existing contracts, and let users interact with nearly identical applications on their own blockchain. This approach requires little incremental development on the part of the application developers, and the application immediately unlocks further throughput at low transaction costs.
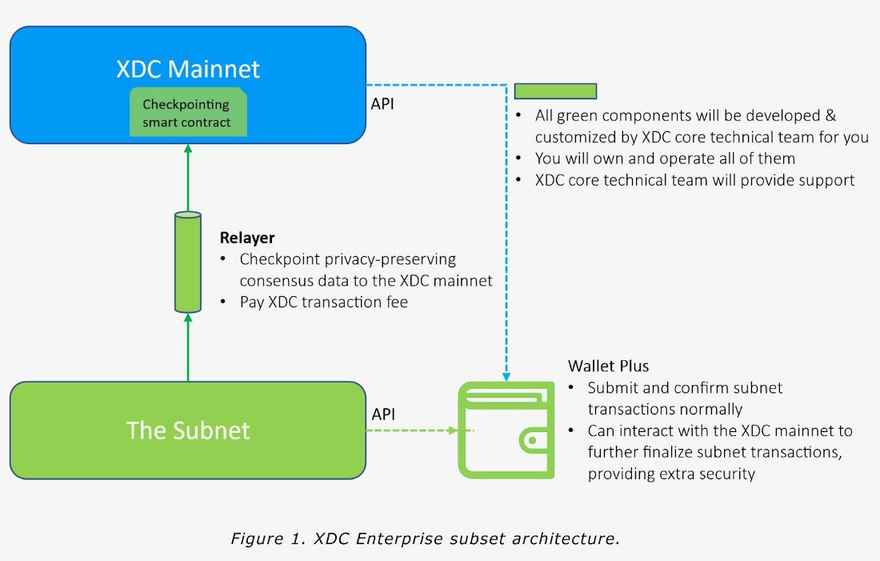
XDC Enterprise Subnet Architecture
The architecture consists of the following key components owned by the customer:
A subnet driven by the XDC2.0 consensus engine, with system configurations tailored for the customer.
A relayer program that checkpoint critical consensus data of the subnet to the XDC mainnet
A smart contract in the XDC mainnet that verifies and records the checkpoints.
Wallet APIs that enable additional protection of subnet transaction from the XDC mainnet
The subnet will also natively support XDC’s abundant utility tools such as blockchain explorer and forensic monitor.
Any enterprise can start the setup of their subnet easily using the guideline from website https://www.xinfin.org/xdc-subnet The XDC Network tech team also provides guidelines through the XDC.Dev tech forum.
The secret sauce — why build on XDC Network?
The XDC ecosystem has grown popular over the past year for a number of reasons, and quite a few strong points are directly applicable to prospective Subnets. Each of the following functionalities can be leveraged by Subnets launching their own blockchain:
Fast finality: XDC consensus mechanism is unique in that it reaches finality on a transaction within a single block, which typically takes 2 seconds on the mainnet. Similarly, Subnets can achieve this fast finality on their blockchains by using the XDC consensus mechanism.
The unbounded number of Masternodes: Allowing more masternodes on a network means more decentralization. XDC consensus mechanism can maintain fast block times while increasing to an unbounded number of Masternode.
Future Subnet Interoperability: Most Subnets will likely want to connect to existing blockchains in order to onboard users. While native interoperability within the ecosystem isn’t available, the XDC team should be building out Cross-Subnet Transfers, bridging XinFin Primary Networks and Subnets.
It’s also important to note that Subnets do not inherit the security or decentralization of the broader XDC network. Not all XDC Masternode will likely validate on any given Subnet, and the percentage of a network controlled by any Subnet validator will depend on the Subnet’s staking dynamics. Subnets need to incentivize their Masternode separately from the XDC network to enhance their security, decentralization, and stability. Also, if a Masternode misbehaves on a Subnet, the Masternode is slashed and punished on the main XDC chain
Why are subnets important in the world of blockchain?
They offer a decentralized and flexible approach to building and deploying decentralized applications (dApps). It also allows for the creation of specialized, independent networks that can serve specific purposes and improve the scalability of the overall network. The major use case here is that of an insurance company that would want to use it to store all of the data of the claims made by their customers. But since this data is confidential and may have private information about users, like their medical history, it cannot store it on a public blockchain. Therefore, using a blockchain subnet to store all that data but having that subnet accessible only by computers and employees internal to that organization is one way to approach these problems.
Future prospects
As decentralized applications have gained traction, popular applications have been limited by the chain they call home. In response, app-specific blockchains have become increasingly popular.
Subnets can also be permissioned, unlocking use cases for more traditional institutions. There must be a subnet incentive program, where they should collaborate with several other teams to create a Subnet designed for institutions leveraging DeFi with native KYC functionality.
In conclusion, the XDC Enterprise Subnet Architecture provides a comprehensive solution for customers to manage their private blockchain network securely. It offers a range of features, including a subnet driven by an XDC2.0 consensus engine, a relayer program to checkpoint critical data to the mainnet, a smart contract in the mainnet to verify and record checkpoints, and wallet APIs to provide additional protection from the mainnet. This architecture supports XDC’s numerous utility tools, such as blockchain explorer and forensic monitor, and will ensure that customer confidential data remains secure.






Discussion (1)
Thank You!