In any programming language, operators play a vital role i.e. they create a foundation for the programming. Similarly, the functionality of Solidity is also incomplete without the use of operators. Operators allow users to perform different operations on operands. Solidity supports the following types of operators based upon their functionality.
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment operators
- Conditional Operator
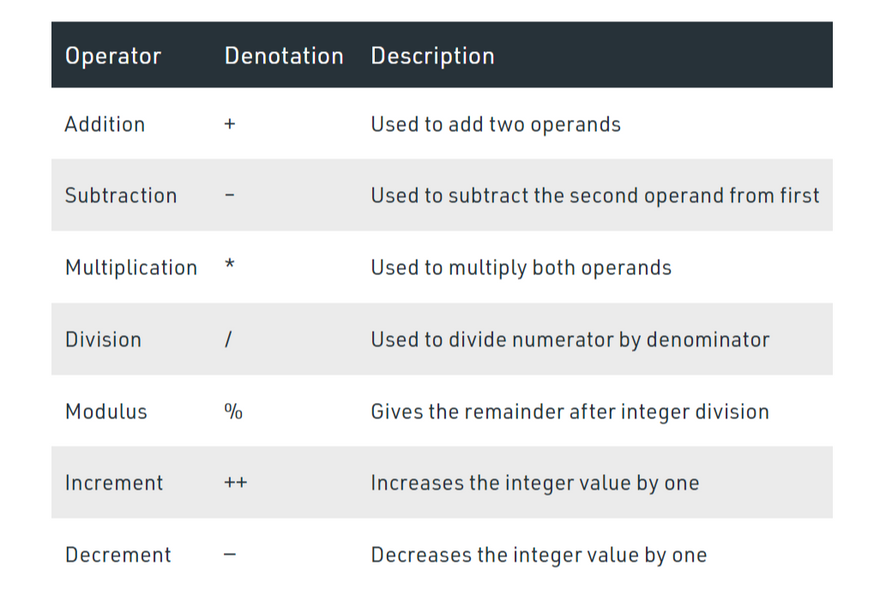
Arithmetic Operators
These operators are used to perform arithmetic or mathematical operations. Solidity supports the following arithmetic operators:
Example: In the below example, the contract SolidityTest demonstrates the above mentioned different types of arithmetic operators.
// Solidity contract to demonstrate
// Arithmetic Operator
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract SolidityTest {
// Initializing variables
uint16 public a = 20;
uint16 public b = 10;
// Initializing a variable
// with sum
uint public sum = a + b;
// Initializing a variable
// with the difference
uint public diff = a - b;
// Initializing a variable
// with product
uint public mul = a * b;
// Initializing a variable
// with quotient
uint public div = a / b;
// Initializing a variable
// with modulus
uint public mod = a % b;
// Initializing a variable
// decrement value
uint public dec = --b;
// Initializing a variable
// with increment value
uint public inc = ++a;
}
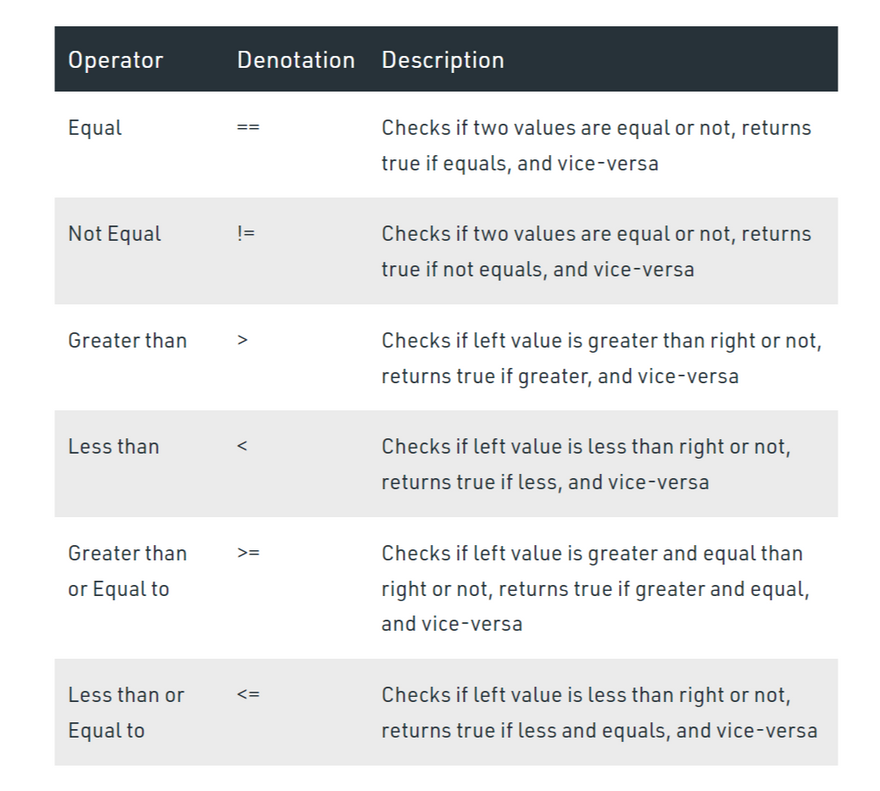
Relational Operators
These operators are used to compare two values. Solidity supports the following relational operators:
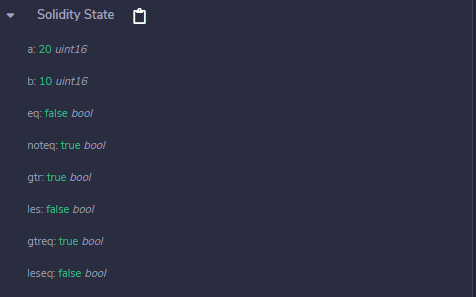
Example: In the below example, the contract SolidityTest demonstrates the above mentioned different types of relational operators.
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Relational Operator
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract SolidityTest {
// Declaring variables
uint16 public a = 20;
uint16 public b = 10;
// Initializing a variable
// with bool equal result
bool public eq = a == b;
// Initializing a variable
// with bool not equal result
bool public noteq = a != b;
// Initializing a variable
// with bool greater than result
bool public gtr = a > b;
// Initializing a variable
// with bool less than result
bool public les = a < b;
// Initializing a variable
// with bool greater than equal to result
bool public gtreq = a >= b;
// Initializing a variable
// bool less than equal to result
bool public leseq = a <= b;
}
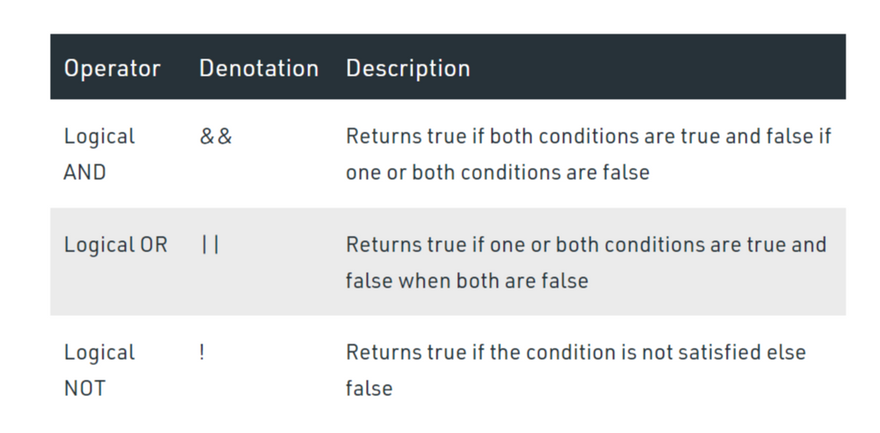
Logical Operators
These operators are used to combine two or more conditions. Solidity supports the following arithmetic operators :
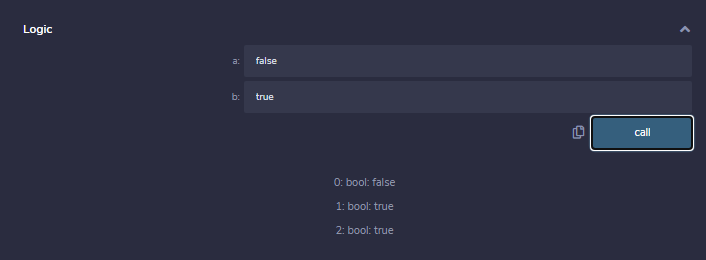
Example: In the below example, the contract logicalOperator demonstrates the above mentioned different types of logical operators.
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Logical Operators
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract logicalOperator{
// Defining function to demonstrate
// Logical operator
function Logic(
bool a, bool b) public view returns(
bool, bool, bool){
// Logical AND operator
bool and = a&&b;
// Logical OR operator
bool or = a||b;
// Logical NOT operator
bool not = !a;
return (and, or, not);
}
}
Bitwise Operators
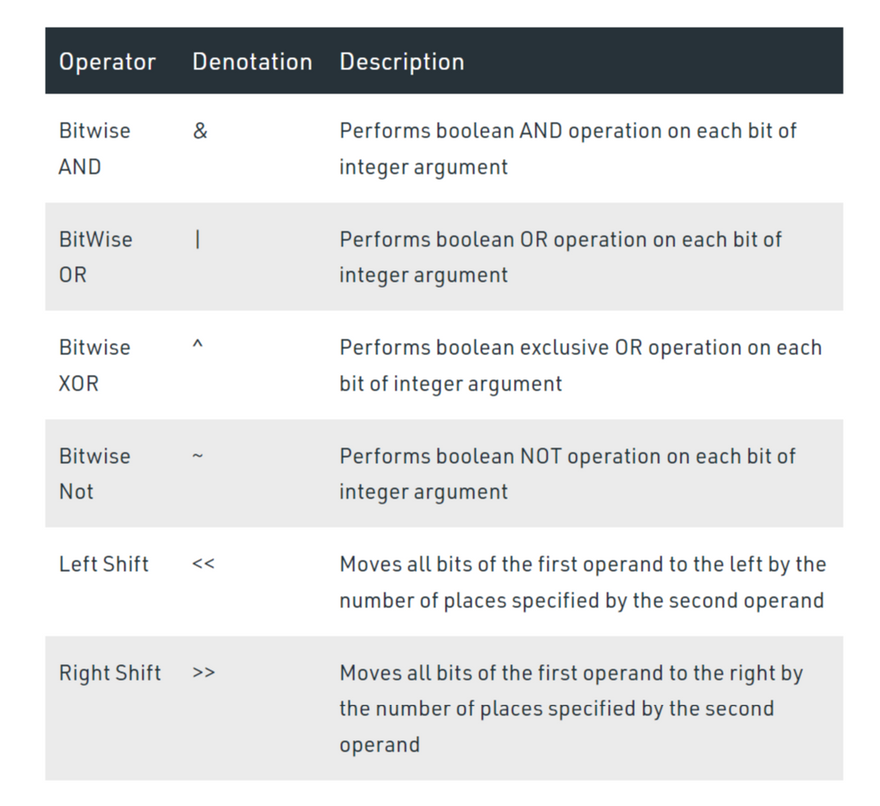
These operators work at a bit level used to perform bit-level operations. Solidity supports the following arithmetic operators:
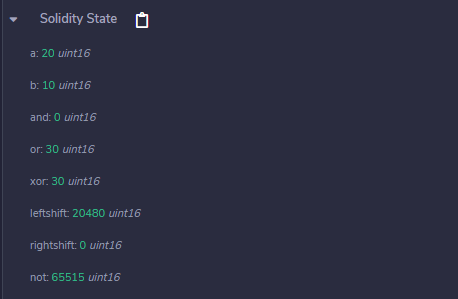
Example: In the below example, the contract SolidityTest demonstrates the above mentioned different types of bitwise operators.
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Bitwise Operator
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract SolidityTest {
// Declaring variables
uint16 public a = 20;
uint16 public b = 10;
// Initializing a variable
// to '&' value
uint16 public and = a & b;
// Initializing a variable
// to '|' value
uint16 public or = a | b;
// Initializing a variable
// to '^' value
uint16 public xor = a ^ b;
// Initializing a variable
// to '<<' value
uint16 public leftshift = a << b;
// Initializing a variable
// to '>>' value
uint16 public rightshift = a >> b;
// Initializing a variable
// to '~' value
uint16 public not = ~a ;
}
Assignment Operator
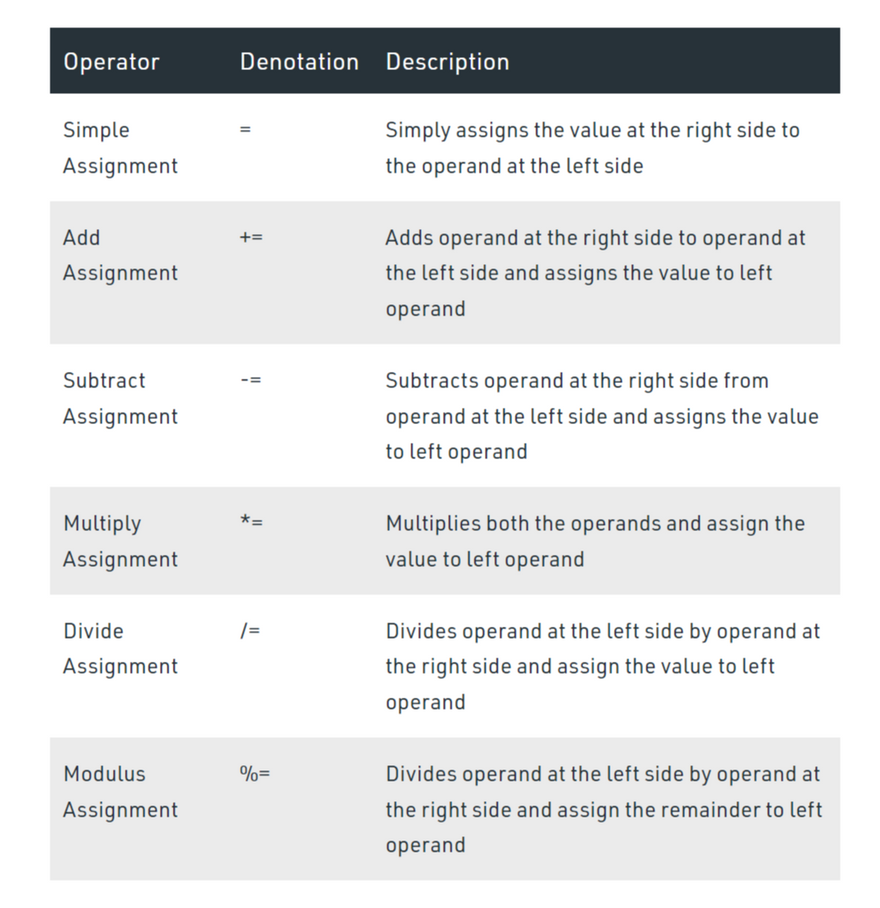
These operators are for the assignment of value to a variable. The operand at the left side is variable while operand at the right side is value. Solidity supports the following arithmetic operators :
Example: In the below example, the contract SolidityTest demonstrates the above mentioned different types of assignment operators.
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Assignment Operator
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract SolidityTest {
// Declaring variables
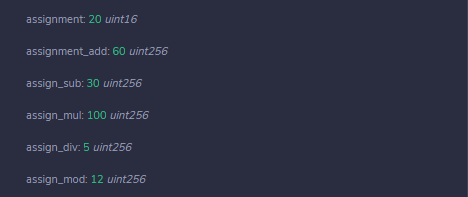
uint16 public assignment = 20;
uint public assignment_add = 50;
uint public assign_sub = 50;
uint public assign_mul = 10;
uint public assign_div = 50;
uint public assign_mod = 32;
// Defining function to
// demonstrate Assignment Operator
function getResult() public{
assignment_add += 10;
assign_sub -= 20;
assign_mul *= 10;
assign_div /= 10;
assign_mod %= 20;
return ;
}
}
Conditional Operators
It is a ternary operator that evaluates the expression first then checks the condition for return values corresponding to true or false.
Syntax:
if condition true ? then A: else B
Example: In the below example, the contract SolidityTest demonstrates the conditional operator.
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Conditional Operator
pragma solidity ^0.5.0;
// Creating a contract
contract SolidityTest{
// Defining function to demonstrate
// conditional operator
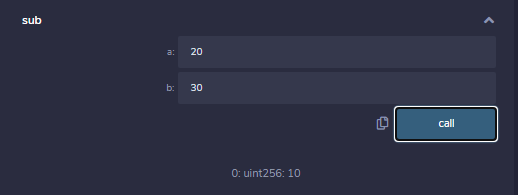
function sub(
uint a, uint b) public view returns(
uint){
uint result = (a > b? a-b : b-a);
return result;
}
}






Discussion (0)